Polyprenol is one of the most common types of polyisoprenoids contained in plants; its chemical formula is H-[CH2-C(CH3)=CH-CH2]n-OH where “n” is the amount of isoprene units. They are unsaturated polyisoprenoid alcohols that metabolise into dolichol inside the liver. When an α isoprenoid unit saturates with the help of α saturation a saturated α polypren alcohol or dolichol is created. A phosphorylated form of dolichol or dolichol phosphate is necessary for the biosynthesis of biologically important N-glycoprotein. Dolichols help to contain the sugar groups in the endoplasmic reticulum, while enzymes add these groups to protein. Moreover, cell receptors that attract hormones and activate enzymes are built on the basis of glycoproteins. Reduced glycoprotein synthesis decreases the chance to repair DNA damage, changes the reactions of the immune system, and the expression of cell biomarkers and signal proteins. Disruptions of the dolichol phosphate synthesis cycle are observed in processes related to ageing, in the case of different pathologies and metabolism disorders. The similarity of dolichol and polyprenol chemical structure and the studies of recent years on the metabolising of polyprenols into dolichols in an animal liver by ensuring the normal operation of the dolichol cycle have produced great interest in the healing potential of polyprenols. Polyisoprenoids can positively influence the levels of lipids, reduce the activity of inflammation and have hepatoprotective properties.
Humans only consume polyprenols through greens as food. Dolichols can be consumed by eating raw animal products. Unfortunately, the preserved foods of today and the deficit of fresh green plants in the diet cannot provide humans with the amount of polyprenols necessary for normal operation of the dolichol cycle.
Polyprenols can only be consumed by eating fresh greens or using special extracts, because they are insoluble in water and spirits, which are used as solvents in the production of extracts.
Carotenoids belong to terpenoids, one of the largest groups of biologically active substances that includes more than 30 000 different compounds, including compounds with taste, smell, compounds that attract insects, and antibiotics.
According to their structure carotenoids are considered to be tetraterpenes. In plants they act in a similar way to chlorophyll in the process of photosynthesis, increase the amount of light that can be absorbed in the pigments of photosynthesis, as well as give a special red or orange colour to plants containing carotenoids (for example, lycopene in red tomatoes, lutein in yellow pepper, and α- and β-carotenes in orange carrots).
Carotenoids are one of the most common natural pigments; they are usually produced by bacteria, fungi and plants. They are very common in vegetation, often encountered in microorganisms and determine the colour of animal skin, bird feathers and water animals.
Carotenoids have a significant influence in the regulation of cholesterol level.
They stimulate the correct circulation of blood.
Carotenoids not only have the functions of provitamin A, they also act as antioxidants.
Carotenoids improve vision, strengthen bones, teeth and nails.
They help to maintain healthy skin and nails and increase the resistance of an organism towards infections.
“Silbiol E” is a concentrate of biologically active compounds extracted from spruce tree extractives. The main components of “Silbiol E” are:
Epimanool not less than 25 %;
Carotenoids ~7 %;
Hydrocarbons ~5 %;
Sterols ~ 17 %;
Including β-sitosterol ~ 10 %;
Esters, aldehydes, oxides ~ 10 %;
Spirits ~ 17 %;
Nonacosanol-10 1 – 2 %;
Other compounds ~ 15 %.
Product is standardised according to the content of the active substance (epimanool).
Qualities of silbiol:
antiviral activity against group A influenza viruses, rhinovirus HRV-13, Samp Long virus, influenza viruses A-H2N2, H3N3 and B/Tokyo/7/66,
bactericidal activity against gram-positive microbes (Staphylococcus aureus 209R, Bacillus subtilis ATSS 6633), as well as fungicidal activity against Candida albicans.
The preparation can be used in food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical products.
Provitamin concentrate is a concentrate of neutral compounds extracted from spruce tree needle extractives. The main components of provitamin concentrate are:
Hydrocarbons 5.3%: (including alkanes 2.2 % and terpenes 3.1 %);
Esters 45.6 %: (including acetate 31 %, di- and triglycerides ~ 10 %);
Aldehyde 0.5 - 1.0 %;
Oxides ~ 0.5 %;
Spirits ~ 33 %;
Polyfunctional, oxygen-containing compounds 9 – 14 %;
Vitamin E (0.5 – 0.6 %);
β-carotene (0.4 – 0.6 %);
Polyprenols (3 – 4 %);
Epimanool (3 – 4 %);
Geraniol (0.1 – 0.2 %);
β-sitosterol (6 – 8 %);
and other compounds.
As a complex of biologically active substances provitamin concentrate can be used in in the production of cosmetics, chemical products and feed additives.
Needle Sodium Chlorophyllin is a concentrate of chlorophyll derivatives (chlorines, phaeophytins, phaeophorbides), obtained from coniferous tree needle foliage extractives. It contains water-soluble chlorophyll derivatives, resin acid and fatty acid sodium salts, and other compounds.
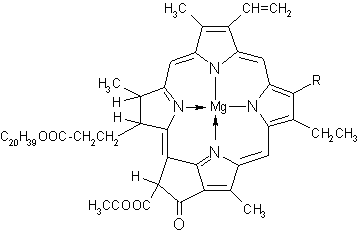

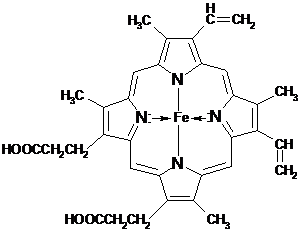
Taking into account the structural similarity of chlorophyll and blood haemoglobin-heme and the results of performed studies, chlorophyllin can be used:
in the case of anaemia, to reduce adverse reactions to chemotherapy and radiotherapy, as it rapidly increases the leucocyte content in the blood.
to reduce risk in the case of tumours, as it shows clear anti-mutagenic and anti-cancerogenic properties.
in the case of asthma, as it has deodorising qualities.
in the case of gastric ulcer and pancreatitis, as it has healing qualities.
in the case of atherosclerosis and psoriasis, as it prevents the further development of these diseases.
to reduce the symptoms of alcohol hangover syndrome.
as a raw material in the production of cosmetic, pharmacy and food products.
Natural essential oils or various essential oil fractionations are produced from ecologically clean pine and spruce tree needles by the method of steam distillation.
Pine essential oils are used as a means of aromatherapy and act as a strong antiseptic, bactericidal and antiviral substance that stimulates blood circulation, increases the bioenergy of an organism, and promotes recovery from influenza, respiratory system diseases, and urological diseases, reduces rheumatic pain and normalises digestive system operation.


